- No.609, Centre Of Huijin Nanxiang, Yinxiang Road, Nanxiang Town, Jiading District, Shanghai, China
- sherry@sanmachines.com
- +86-18616767021
3D Printing vs. Laser Cutting!
When it comes to modern manufacturing, technologies like 3D printing and laser cutting are imperative for helping bring designs to life. Both methods offer unique advantages and are often used across various industries, but understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the most suitable option for your project.
What Is 3D Printing?
3D printing constructs objects layer by layer from digital designs. It involves depositing material, such as plastic, metal, or resin, in precise increments to build up the final product. This method allows for intricate geometries and customisation, making it ideal for prototyping, small-scale production, and creating complex shapes.
What Is Laser Cutting?
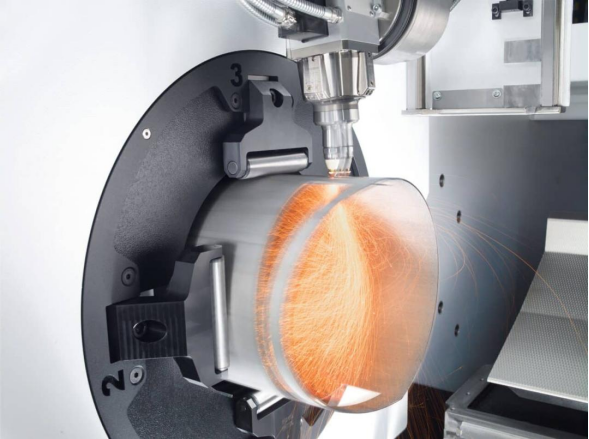

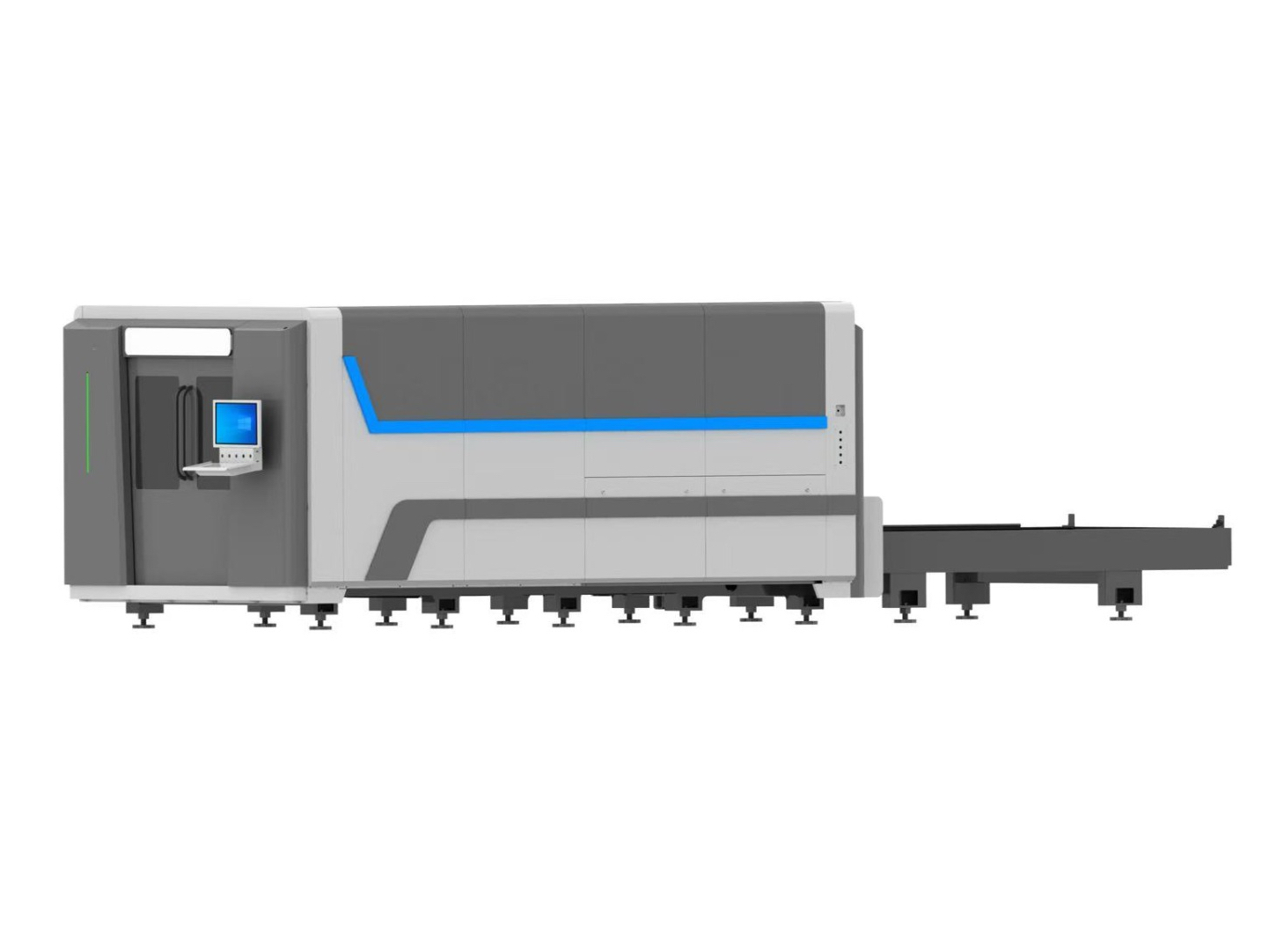
Laser cutting is a manufacturing process that utilises a high-powered laser beam to cut through materials with precision. Unlike traditional cutting methods, which rely on physical tools, laser cutting employs a focused beam of light to vaporise or melt materials along a predetermined path. This technology is commonly used on various materials such as metal, wood, plastic, and fabric, allowing for intricate and accurate cuts. Laser cutting is favoured for its speed, versatility, and ability to create detailed designs, making it a popular choice for a range of industries.
3D Printing Vs. Laser Cutting – What Are The Differences?
l Additive Manufacturing Vs. Subtractive Manufacturing
The fundamental contrast between 3D printing and laser cutting lies in their manufacturing processes. 3D printing operates on the principle of additive manufacturing, where the material is added layer by layer to form the desired object, whereas laser cutting is a subtractive manufacturing method that involves removing material from a solid block to shape the final product.
Versatility and Complexity
3D printing shines in its versatility and ability to produce intricate designs with minimal constraints. It excels in crafting prototypes, customised products, and components with complex geometries, offering designers unprecedented freedom. On the other hand, laser cutting is preferred for its precision and speed in fabricating flat sheet materials or metal tubes. It is widely used for producing parts with sharp edges, intricate patterns, and high dimensional accuracy.
Material Compatibility
While 3D printing supports various materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites, the range of options may vary depending on the printing technology and equipment. Laser cutting, on the contrary, is particularly suited for sheet metals such as steel, aluminium, and brass, as well as non-metallic materials like wood, acrylic, and fabric.
Production Volume and Efficiency
When it comes to large-scale production, laser cutting often proves more efficient due to its rapid processing speed and ability to handle high volumes of identical parts. Additionally, laser cutting offers cost-effective solutions for projects requiring repetitive cutting patterns or standardised components. Conversely, 3D printing may be better suited for low-volume production, intricate designs, or scenarios where customisation is paramount.
Related product links

































 Cutter News
Cutter News