- No.609, Centre Of Huijin Nanxiang, Yinxiang Road, Nanxiang Town, Jiading District, Shanghai, China
- sherry@sanmachines.com
- +86-18616767021
Round Guide Rails VS Square Guide Rails for CNC Routers!
Round Guide Rails
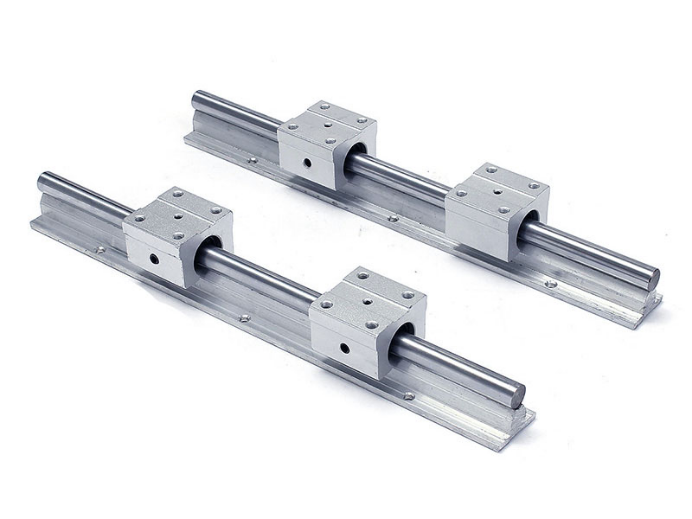

Before the advent of Square guide rails, Round guide rails were expected to satisfy every linear motion-control situation. And for many years, they did so admirably. But as CNC router tool users demanded closer tolerances for certain jobs, CNC router makers favored the classical method of milling and scraping ways. Round guide rails were used for peripheral equipment when they couldn't meet tolerance requirements.
This didn't make Round guide rails less valuable or obsolete. Their benefits continue to outweigh their drawbacks. Round guide rails are generally less expensive than Square guide rails, but that should not be the primary criterion for any application. A square rail can actually fail whereas a round rail can work smoothly and flawlessly. For example, Round guide rails are more forgiving of misalignment, poor parallelism, and moment loads in most CNC machines and allow more variation in rail height than square-rail systems. Still, they can hold a travel straightness of 0.01-in. for 10 ft. Also, the small rolling element tends to make the round-rail motion smoother.
To attain this accuracy, they need support only at the ends, although many are supported at several points or along their full length. This lets the rails cross over gaps without a problem, and safely go from one support to another. When the round-rail system requires only a shaft-rail assembly (a shaft, a rail, or a shaft and two end-supported blocks with four pillow blocks) the preparation cost is less than the square rail. Generally, round-rail installation is relatively easy and inexpensive. And Service and replacement favor the round rail.
Square Guide Rails (Profile Guide Rails)
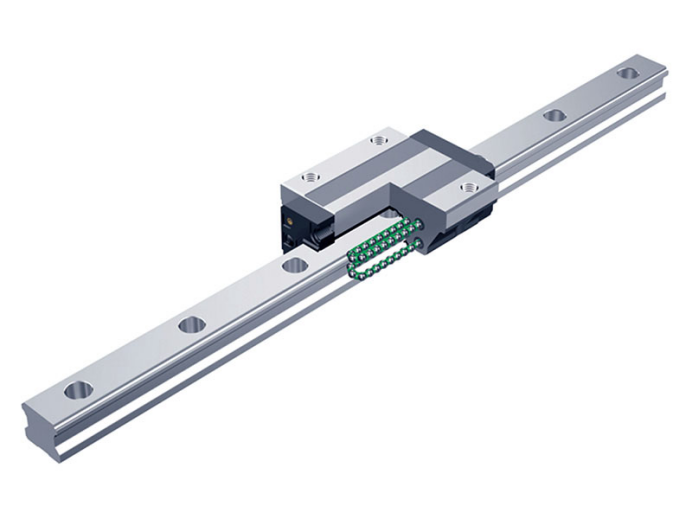
Square guide rails were initially designed for the CNC router tool industry. They replaced integrated carriages and ways, which are integral areas of the CNC router bed. Notwithstanding, some traditional carriages and ways still provide high accuracy in certain situations.
Square guide rails are stiffer and more rigid, but need straight, continuous support with tight requirements for flatness and parallelism; they can't span the gaps that a round rail can. However because CNC router manufacturers are accustomed to precision bed preparation, this isn't a problem.
The main advantage of Square guide rails is their high positioning accuracy, especially useful in milling and grinding. They hold from 0.0002 to 0.001 in. over a length of 10 ft, compared to 0.01 in. for Round guide rails. They also handle this precision for a moment load; a single carriage and single rail are better suited for this than a round rail. And because the square rail handles higher loads at high accuracy, most users tolerate somewhat less smoothness than the Round guide rails offer.
Although a single profile rail unit can handle a moment load, it's not always recommended. Two or more units should be used to balance the load or distribute the weight. However, one square rail can fit where two Round guide rails would be required. Profile rails are also easier to use because they need one or two parts for a complete system, the rail, and the carriage, whereas the round rail comprises a few more parts.
Square guide rails have higher load-life capacity, defined as the amount of load the unit survives traveling a specified distance. For example, a 20,000-N capacity is based on a 100-km rating. And the wear is minimal because the rail doesn't slide but has rolling contact. Square-rail life primarily depends on the type of environment in which it resides, proper lubrication, and maintenance. With all else being equal, Round guide rails are a little more tolerant because they are not as tight a package and not as sensitive to slight variations. A square rail is more sensitive to debris and impact, although it does have a higher capacity and resistance to impacts that don't affect the rolling element.
Considering the wear aspect, the round rail also has natural debris-shedding capabilities. Square-rail tracks are hidden from direct access but do not necessarily shed debris. With a fluid driving force applied to the rail, a round rail performs better than a square rail, because the square rail could pull up on some of the race areas, whereas the round rail has fewer tendencies for pull-up.
Select a type of rail to use before starting the CNC router component layout. The mounting fixtures are radically different between round and Square guide rails, and the area in which to work varies as does the load rating for the physical size. If it doesn't work out later, changing from one brand of square rail to another is easier than changing from a square to a round rail. All manufacturers follow standards that allow some degree of interchangeability within a type.
Efficiency can be approached from two angles. One deals with the drag coefficient of friction; less friction means lower input energy. Round-rail drag is a little lower and its action is smoother than a profile rail. But those who use Square guide rails regularly provide enough power to drive the rails sufficiently well. Some also consider efficiency from the standpoint of overall envelope or size. The smaller profile rail offers a smaller package for higher loads.
Shock loading, as with an instantaneous impact load, affects all bearings. Square guide rails can handle a heavier load than a small unit, so the shock is more of an impact force. But in all cases, the rail is scaled to the capacity of the normal load, not a shock load. There is no significant difference except that in heavy machinery a shock is more detrimental just because of the pure mass.
Square guide rails come with some critical environmental deratings, typically found in the manufacturer's handbook or design guide. Unfortunately, designers don't consider derating factors frequently enough in the beginning design stages for either round or Square guide rails. For example, the standard duty-cycle rating in the U.S. is 2 million in. or 50 km and 100 km or 4 million in. for the European market. Often, the standards recommend that a rail system not be used beyond either 25 or 50% of the rated capacity.
Related product links


































 Cutter News
Cutter News