- No.609, Centre Of Huijin Nanxiang, Yinxiang Road, Nanxiang Town, Jiading District, Shanghai, China
- sherry@sanmachines.com
- +86-18616767021
The workings of laser welding machines and the unique traits of each type of laser!
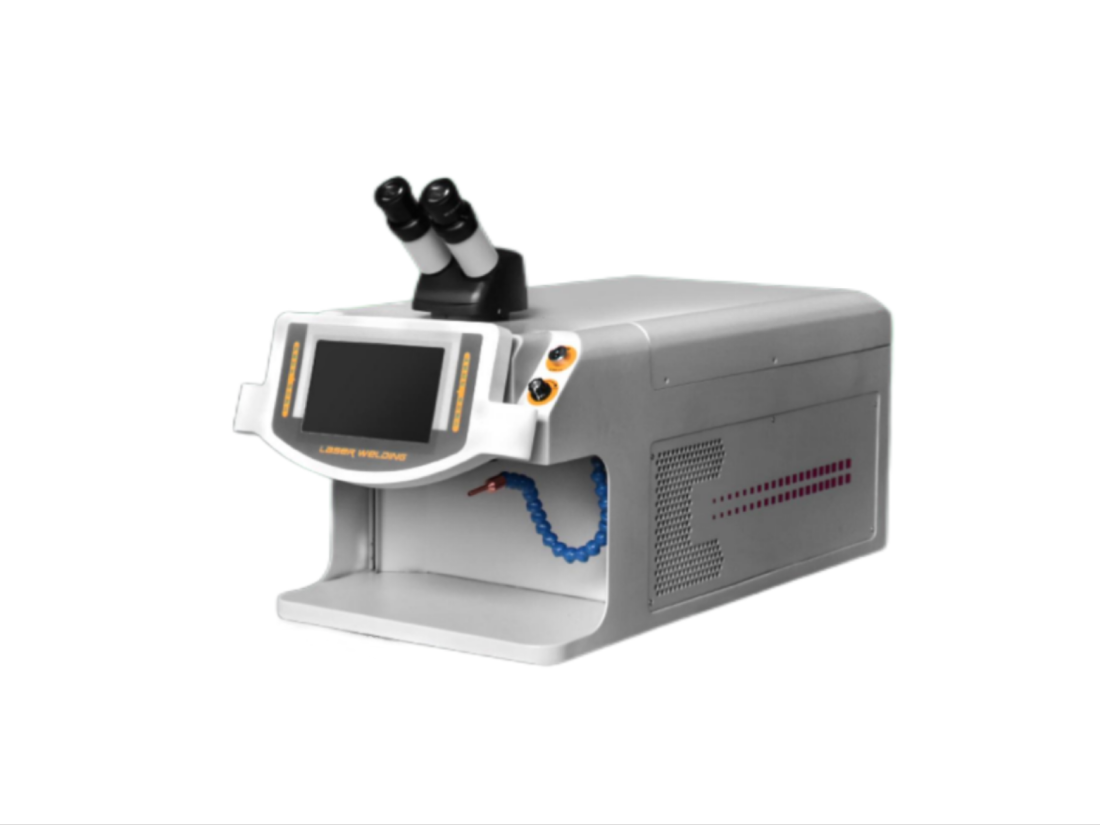
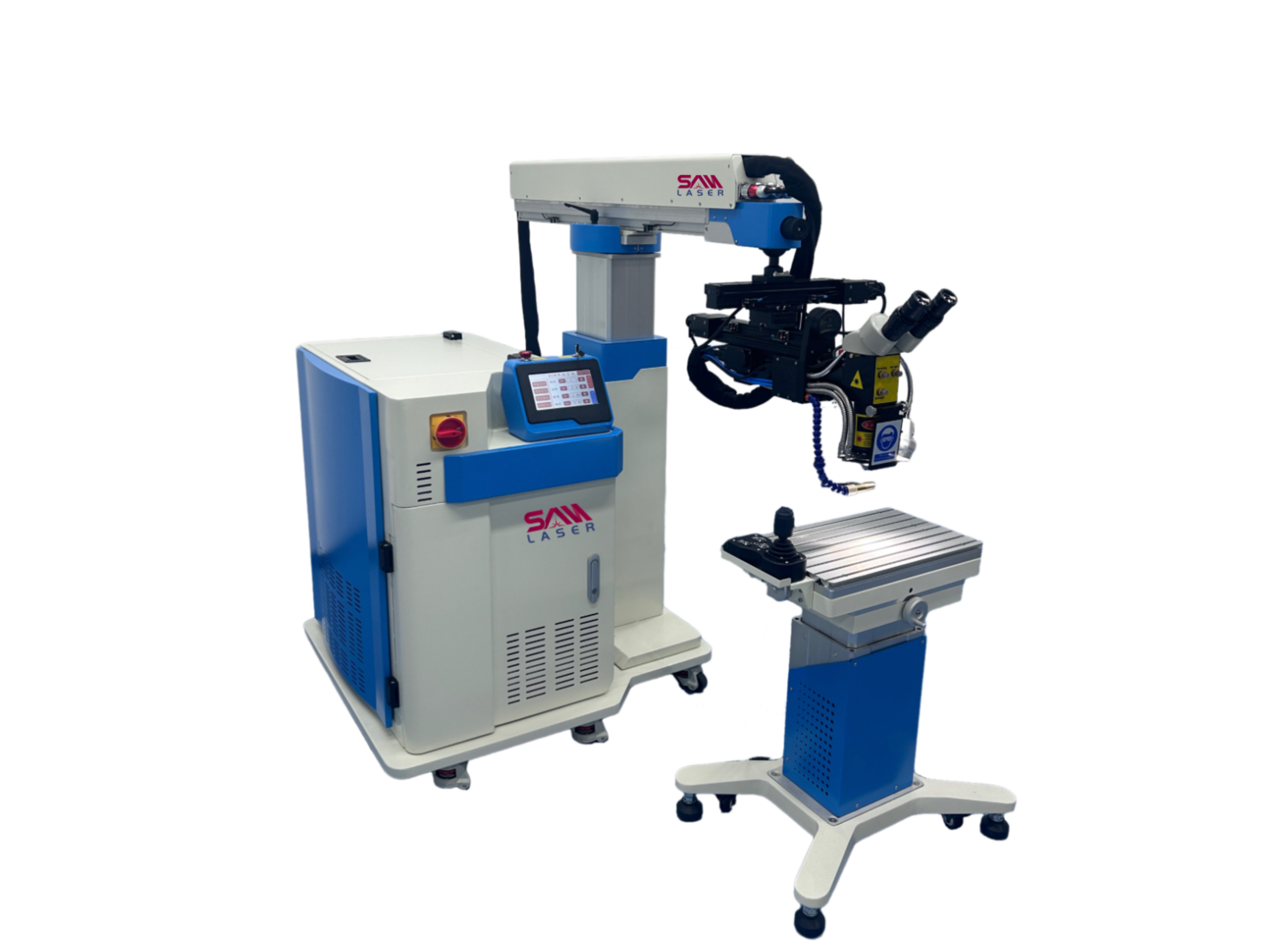
A laser welder is a welding machine that uses a focused beam of high energy light to fuse materials together. It works by shining a focused beam of laser light onto the surfaces of the materials to be welded, forcing them to melt and fuse together at the point of contact. Laser welders are quite well-known for their precision, speed, and versatility, making them ideal for a wide range of applications across industries. They are widely employed in manufacturing processes for metals, polymers, and other materials that demand high-quality and precise welding.

Let’s break down the basic operational structure:
Operation structure of laser welding machine
1.A laser oscillator emits laser light, acting as the machine’s energy source
2.This laser light travels along an optical path
3.A focusing unit, like a focusing lens, concentrates the laser light into a spot system
4.The focused laser light is then directed onto the material placed on the workbench
The above is the basic process. In addition, a process may be added to blow out shielding gas to prevent oxidation and nitridation of the welded area.
5 unique laser types
The most important point in the above structure is the type of laser light. Laser welding machines can be roughly divided into the following five types.
· CO2 Laser
· YAG Laser
· Fiber Laser
· Disc Laser
· Semiconductor Laser
Let’s break this down and explain the 5 different types of lasers.
CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) Laser
The CO2 laser stands out as a prominent example of gas laser welding. Its defining characteristic lies in utilizing carbon dioxide as a medium to amplify light. In particular, it is possible to perform uniform and high-strength welding when welding materials with a thickness of 10 mm or more or over large areas of several tens of square centimeters or more. It is also possible to weld resin, etc., so it is used in a wide range of fields.
Another feature is that capable of stable continuous operation for long periods of time, allowing continuous work to be carried out on large-scale production lines. CO2 lasers are mainly used in the automotive industry but also play a pivotal role in advancing manufacturing processes.
YAG Laser
The YAG laser is a great example of solid-state laser welding technology. It uses a crystal with a garnet structure as its medium. Due to its characteristics as a pulsed laser, it repeats blinking at small time intervals. Because the wavelength is shorter than that of CO2 laser, energy absorption rate by metal is high and welding is easy.
In addition, it has excellent coherency and laser spreading performance, and is easy to use as it has excellent laser light collection and diffusion. These qualities make them well-suited for welding precision components and delicate tasks.. YAG lasers are mainly used in medical device manufacturing.
Fiber Laser
A fiber laser is a type of solid-state laser that uses an optical fiber as its medium. Its remarkable efficiency comes from confining light within a slender fiber and then amplifying it, enabling exceptionally clean welding.
With a short wavelength and the capability to narrow down the spot, fiber lasers boast high energy density, facilitating deep penetration into highly reflective materials like aluminum and copper. It is also used for welding dissimilar metals together.
Another attractive feature is the ease of automation, such as non-contact, high-speed welding and the ability to automatically set the beam focus. In addition, there tends to be a wide range of products, including handy (hand) torch types and types with cutting, burn removal, and cleaner functions. Fiber lasers are widely used in general industrial products.
Disc Laser
A disk laser is a type of solid-state laser. A crystal doped with rare earth elements such as ytterbium is used as the medium.
These lasers are designed with the aim of overcoming a common issue found in solid-state lasers: a decline in welding accuracy. Traditional solid-state lasers encounter a challenge where heat generated during operation causes uneven temperature distribution in the laser crystal, leading to a thermal lens effect. This effect occurs because the crystal’s refractive index behaves akin to that of a lens, resulting in reduced laser focusing power.
Disk lasers solve this problem by making the laser crystal into a thin disk shape and attaching a heat sink to the back, resulting in higher welding accuracy than previous solid-state lasers. Disk lasers are commonly used in the aerospace industry.
Semiconductor Laser
A semiconductor laser is a type of solid-state laser. Mainly semiconductor materials are used as the medium. It’s also known by other terms such as diode laser or laser diode.
What sets semiconductor lasers apart is their unique heat source: the laser light generated when an electric current passes through the semiconductor. Since it does not use a lamp as the excitation (supply) source, it can be used even in limited spaces.
It is also suitable for very detailed welding work. Semiconductor lasers are commonly used in electronics manufacturing.

































 Welder News
Welder News