- No.609, Centre Of Huijin Nanxiang, Yinxiang Road, Nanxiang Town, Jiading District, Shanghai, China
- sherry@sanmachines.com
- +86-18616767021
A short story about laser cutting machine configuration!
At first, the method for using a laser cutter was to manipulate the workpiece by hand. It was positioned, the cut was made, the laser removed, and the next cut was made. At the time, CNC programming and other technological advances did not exist. Modern laser cutting has removed the need for manual positioning of the workpiece and uses computer-controlled equipment to quickly and efficiently make the proper cuts.
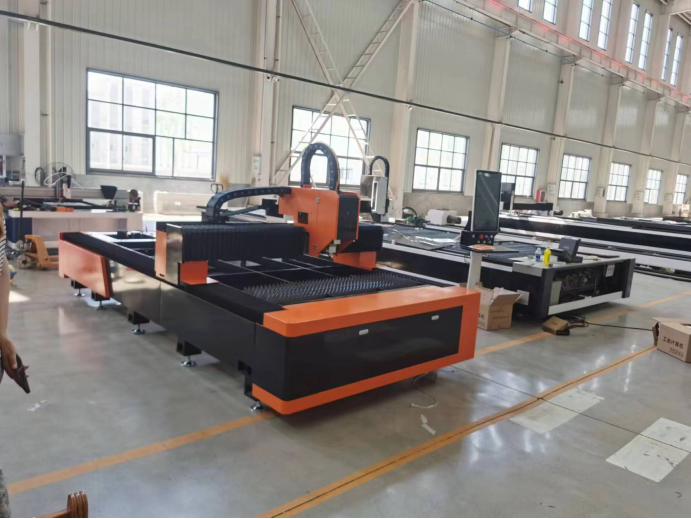

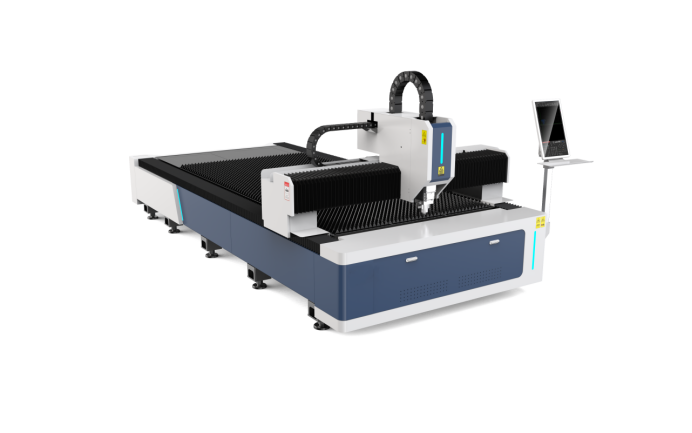
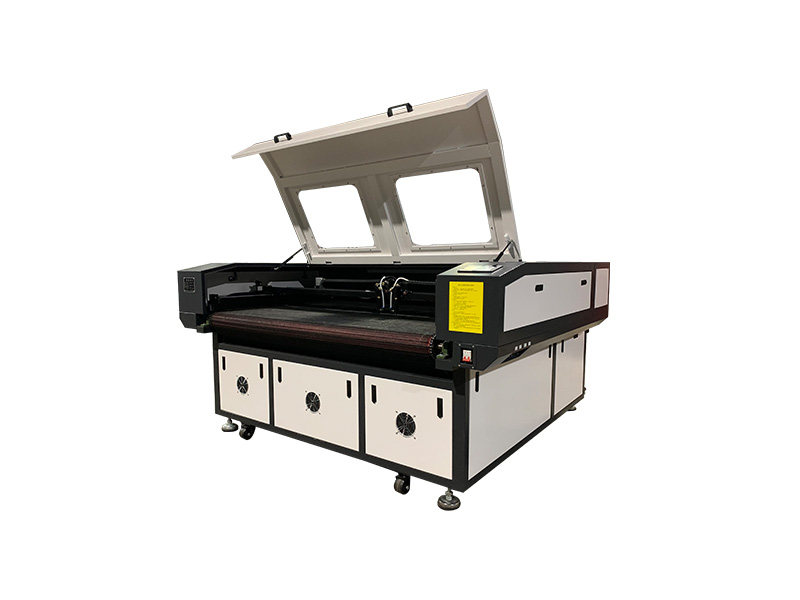
Gantry Laser Cutting Machines
The main types of gantry laser cutting machines are made of aluminum, They have a long horizontal bed and a gantry positioned over the bed. They can be programmed with multiple cuts that are performed with one pass of the laser, which can be a fiber optic or CO₂ laser. Gantry machines use CNC-controlled programming to produce efficient and accurate cuts quickly and easily. Unlike hand manipulation machines with 8 foot to 16 foot (2.4 to 4.9 m) footprints, gantry machines have a footprint of 4 feet to 8 feet. (1.2 m to 2.4 m).
Moving Material Configuration
In this setup, the laser cutter is stationary while the material surface moves. Since no movement from the laser is required, the optics system is simpler than other configurations. However, this is slower than other methods and is usually limited to cutting flat materials.

Flying Optics System
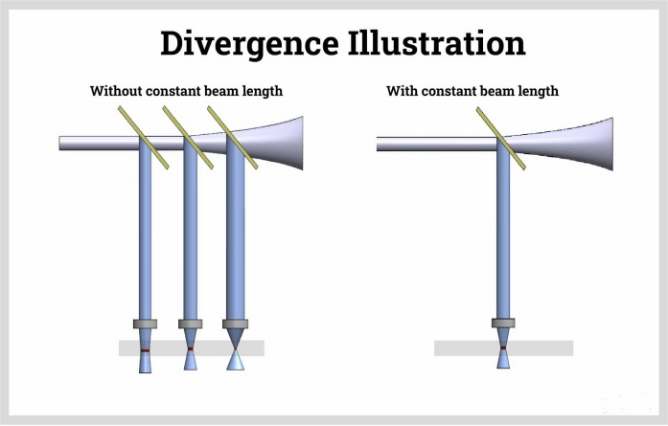
This setup is the opposite of the moving material configuration. The flying optics system involves a stationary material and a movable laser cutter. Since the laser is constantly moving, the laser beam length must be adjusted constantly as well because of the divergence of the laser beam. Greater divergence produces a poorer quality of cut. To mitigate this, re-collimating optics and adaptive mirror control are used. This setup is the fastest of the three since the movement of the mirrors is easier to control.
Hybrid System
In the hybrid system, the material moves on one axis while the optics move on the other axis. This setup combines both advantages and disadvantages of the previous two setups. One advantage of this system from flying optics is that hybrid systems provide a more constant beam path, which reduces power losses.
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Laser Cutting
CNC laser cutting uses a high powered laser beam to mark, cut, shape, engrave, and form material. It is a highly accurate cutting technique capable of shaping small holes and intricate designs. As with all types of CNC machines, CNC laser cutters use the G codes and M codes created for CNC programming as instructions for tool movement and performance.
Unlike traditional CNC machining, CNC laser cutters are non contact and thermal based with a laser head that contains a focusing lens and nozzle. The nozzle, with the lens and head, focuses high intensity light at the workpiece to melt and cut it. Compressed gas flows through the nozzle to cool the lens and remove vaporized metal.
Types of CNC Laser Cutting Machines are:
· CO₂ - A CO₂ laser cutter is a gas laser that uses carbon dioxide as the laser medium.
· Fiber - Fiber laser cutters use diodes to create the cutting beam that is focused through a fiber optic cable. The process produces faster and cleaner cuts.
· Crystal - Crystal laser cutters use beams produced by the crystals of neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) and neodymium-doped yttrium ortho-vanadate (Nd:YVO).
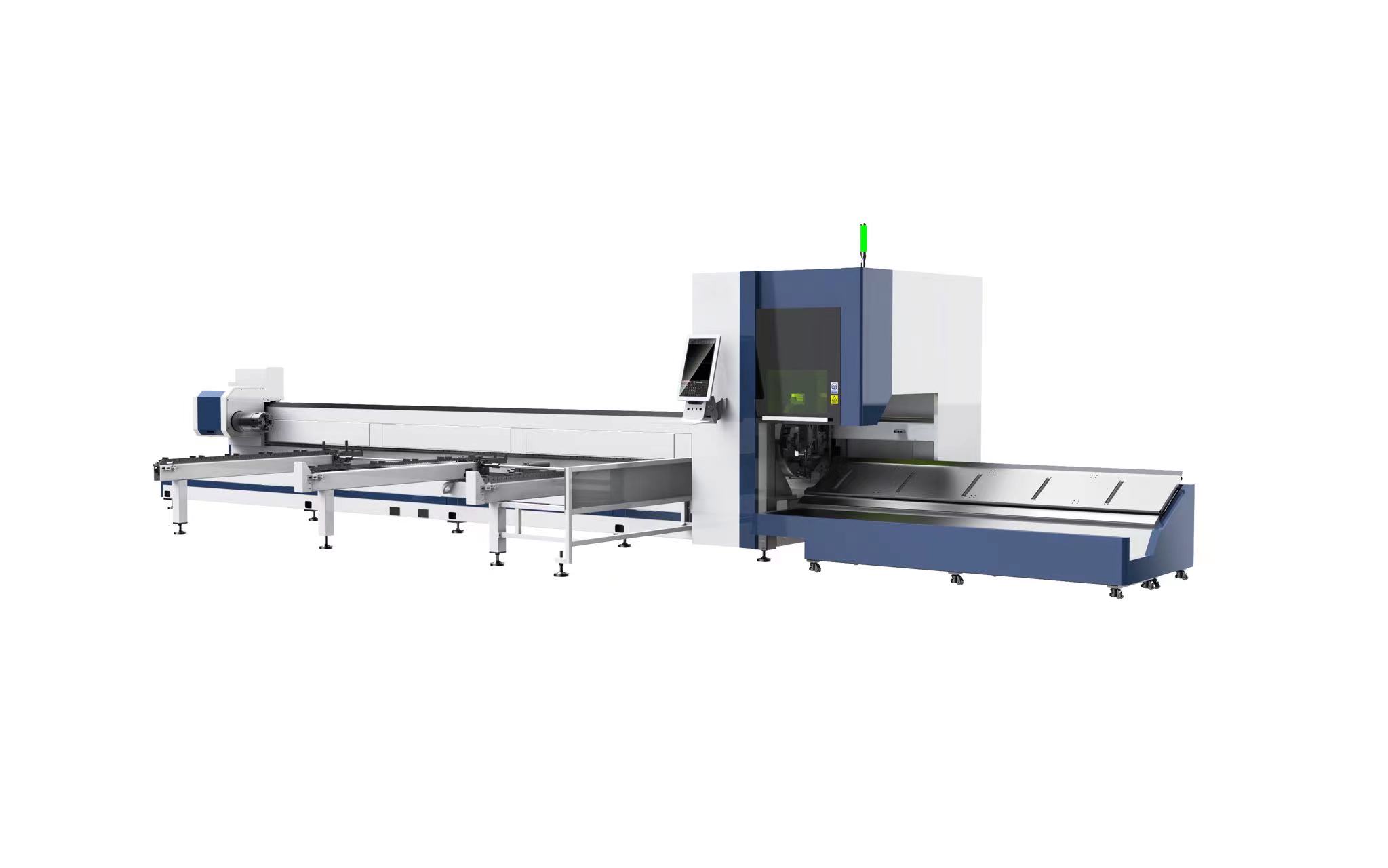
5 Axis Laser Cutting
The process of 5 axis laser cutting makes it possible for the tilting and rotating of the workpiece on the table, which enables the laser to work on three dimensional components that need drilling and cutting on difficult to reach curved surfaces at extreme angles. The use of 5 axis laser cutting reduces the time required to adjust the workpiece to complete the cutting process since the performance of multiple setups increases the possibility of errors.
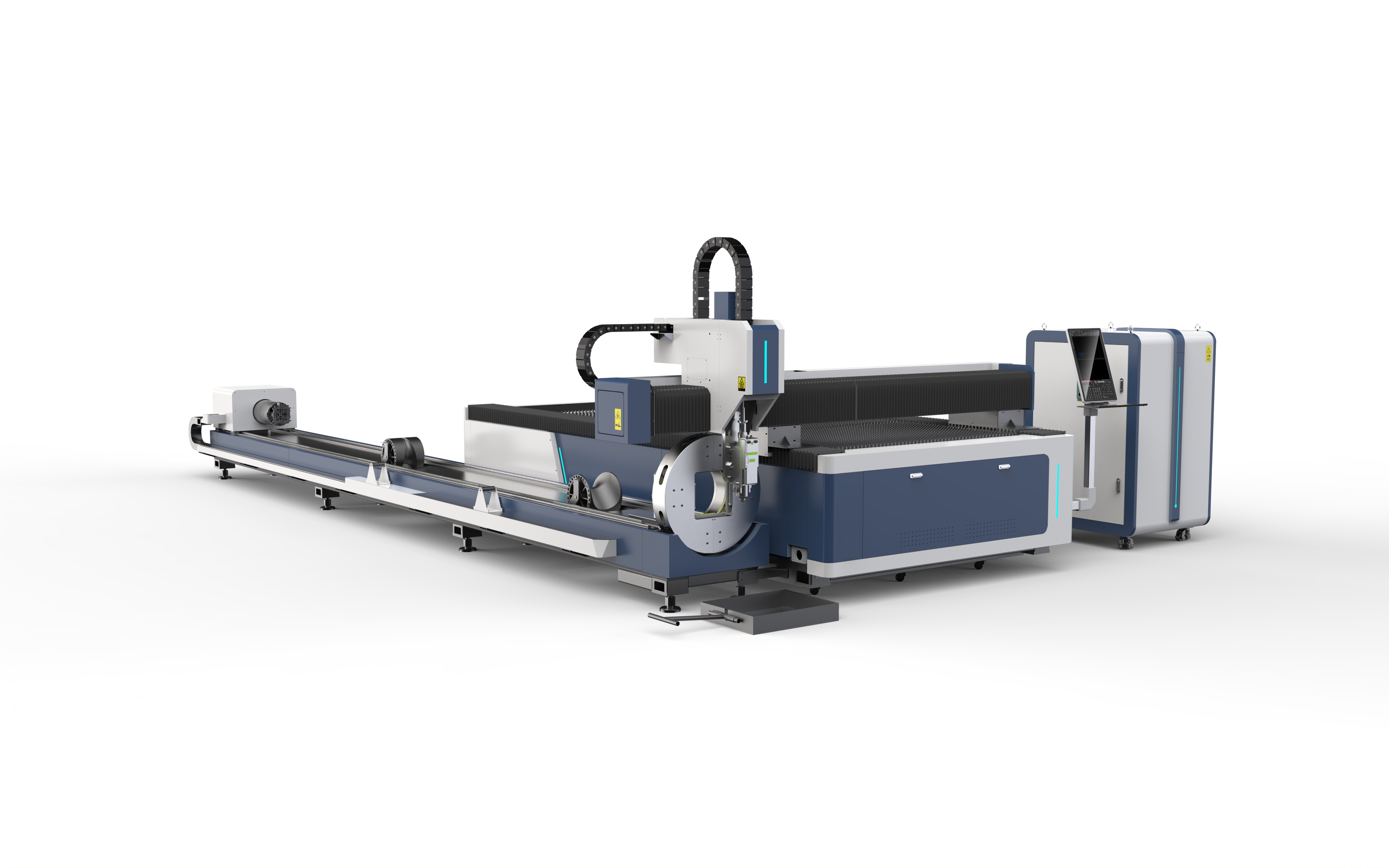
Rotary Laser Cutting
A rotary laser cutter uses a rotating device that positions the workpiece such that it can cut along curved surfaces. The rotary component is a motorized attachment that rotates the workpiece during the cutting process and enables the cutter to make 360 degree cuts and engravings on pipes, tubes, bottles, elliptical tubes, and D shaped items. They are capable of placing intricate designs, logos, patterns, and information on curved surfaces. As with all forms of lasers, the process is performed with high efficiency and precision.

Small Format Laser Cutting
The term small laser cutting, or small geometry laser cutting, refers to design features that are intricate and small. Small geometry laser cutters are used for projects that are too small to be cut by regular cutting methods and are used to avoid loss of resolution. The use of the process applies to parts with features that are smaller than the width of the kerf.
Small geometry laser cutting has exceptional precision that makes it possible to create delicate designs with high tolerances. The thickness of the material determines when small format or geometry laser cutting is used since the use of large laser cutters can impact the final product. Additionally, the use of small format geometry laser cutters is dependent on the size of the feature to be cut, which can be smaller than the kerf of 0.1 mm (0.0039 in).
Large Format Laser Cutting
Large format laser cutting is used when the feature to be cut is an enlarged version of an ordinary feature. The process of large format laser cutting is defined as a project that is larger than the workspace. A large format laser cutter can have a workspace of 3.2 m by 8 m (10.5 ft by 26.25 ft) and is designed for cutting extremely large materials.
Flatbed laser cutting systems are used for large format cutting with bed sizes ranging between 1.3 m by 2.5 m up to 2 m by 3 m (4.3 ft by 8.2 ft up to 6.56 ft by 9.84 ft). The size of a flatbed laser cutter makes it possible to place the material in the processing area for automatic cutting and engraving.
Flatbed Laser Cutter
Flatbed laser cutters are large format laser cutters capable of cutting metals, cloth, wood, and various materials. They can cut a single large feature into a large piece of material or multiple features into several pieces. Flatbed laser cutters have a large flat, horizontal surface for the placement of materials. The laser is enclosed in a mechanism that moves along the sides of the bed as the laser moves back and forth over the cutting surface.
The laser for flatbed laser cutters can be CO₂, fiber, or crystal. The choice of which type of laser to use in a flatbed laser cutter is dependent on the material to be processed with CO₂ lasers used for non-metallic materials while fiber lasers are used for metals. Flatbed laser cutters can have materials continuously fed as part of a production or assembly operation.
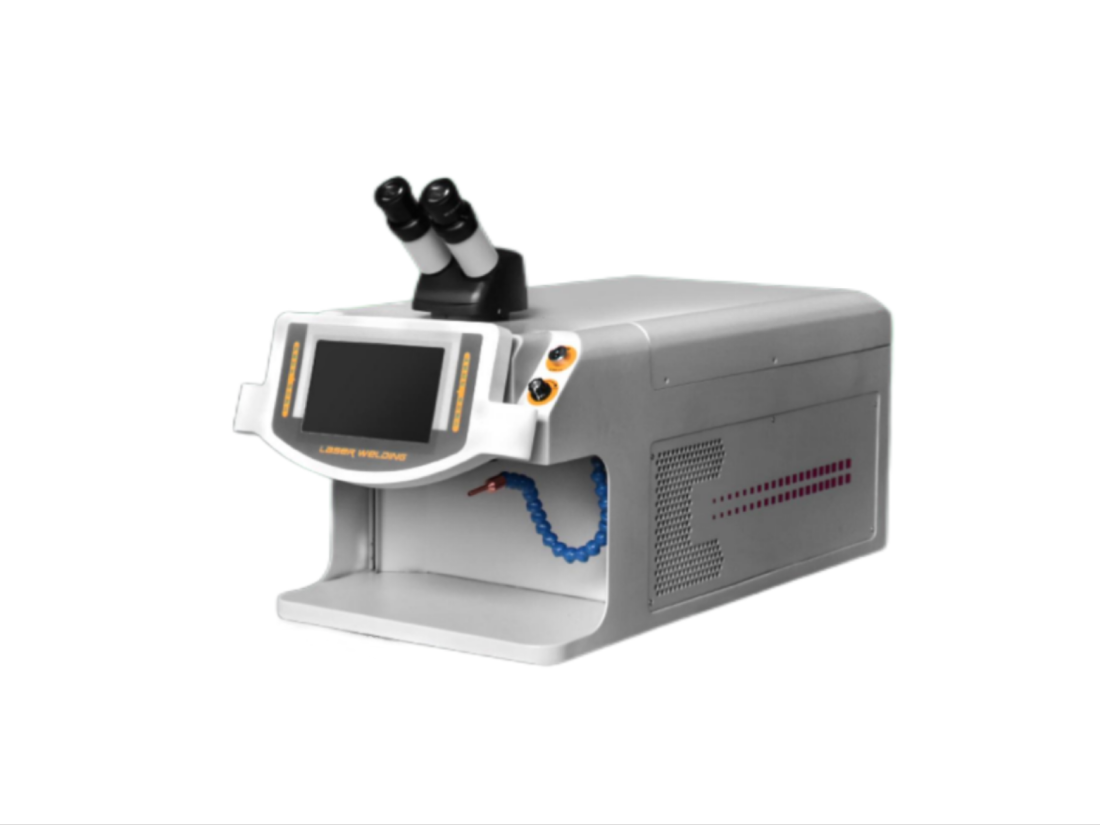
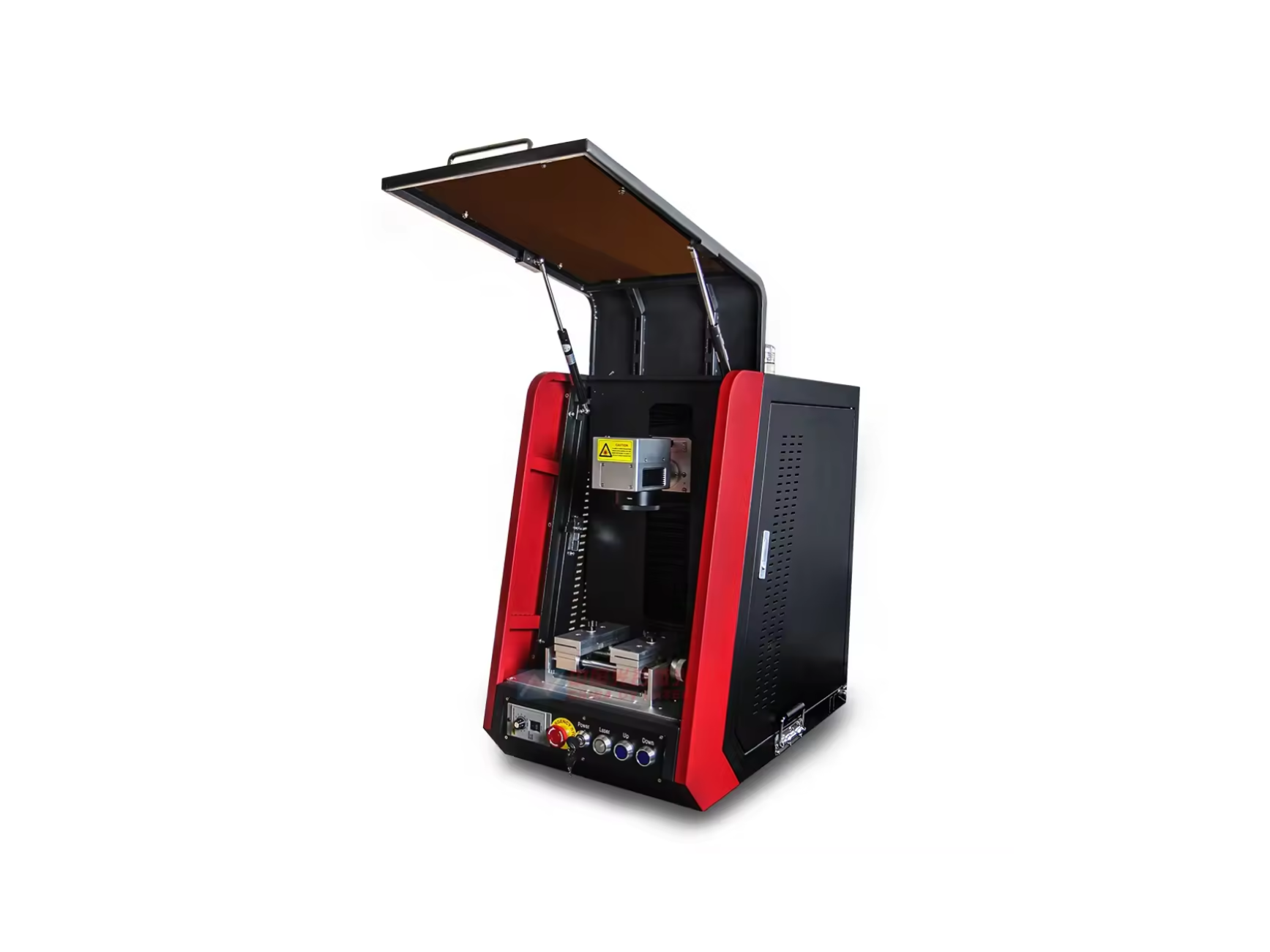
Galvo Laser Cutter or Galvanometer Laser
Galvo laser cutters deflect the laser beam using mirrors that move the beam in different directions by rotating, adjusting, and repositioning mirror angles. The processing by galvo laser cutters relies on the galvanometer that detects and measures electric current by moving a magnetic field.
A galvanometer laser detects electric current and directs the laser to the marking surface using a system of mirrors. The design of galvo lasers makes it possible for them to rapidly complete the engraving process, which is much faster than a traditional laser that moves along the X and Y axis at a slow speed. More area of the workpiece is marked at a higher rate. The key factor is the quick repositioning of the mirror angles in relation to the cutting surface.
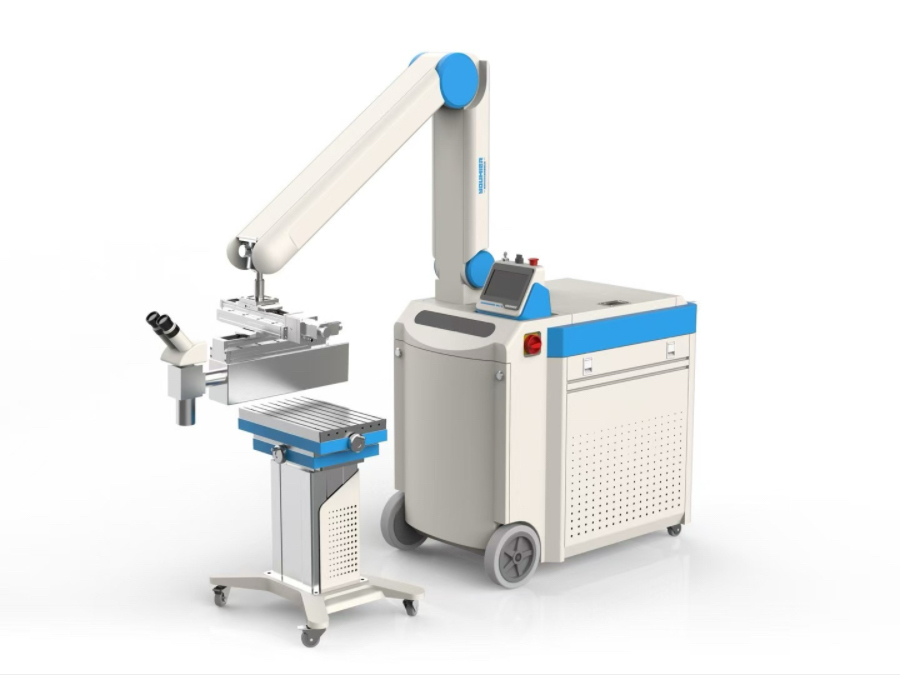
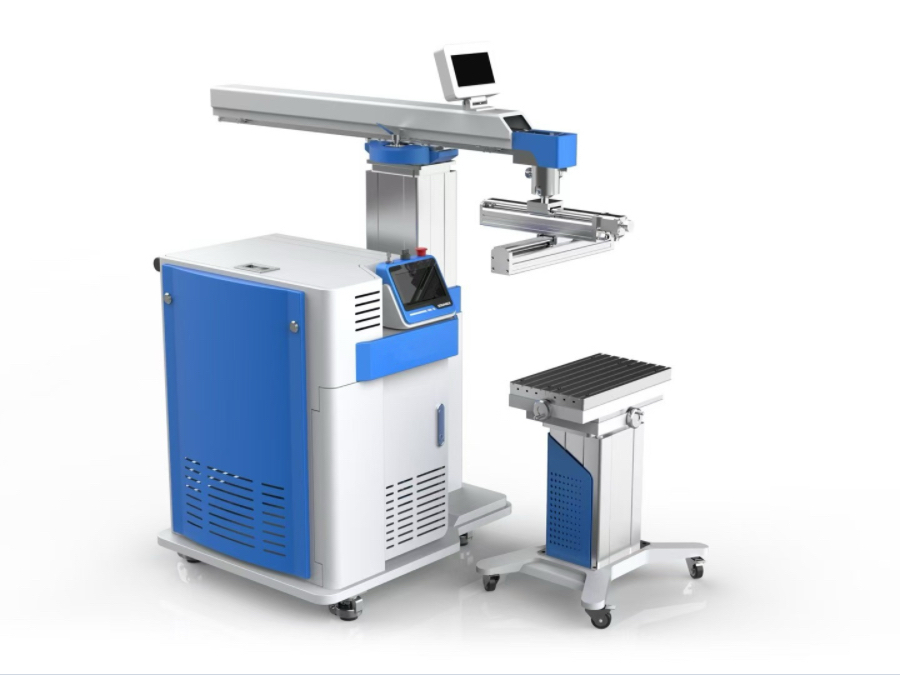
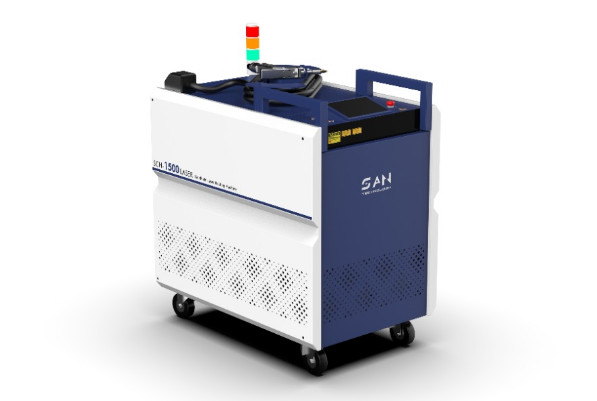
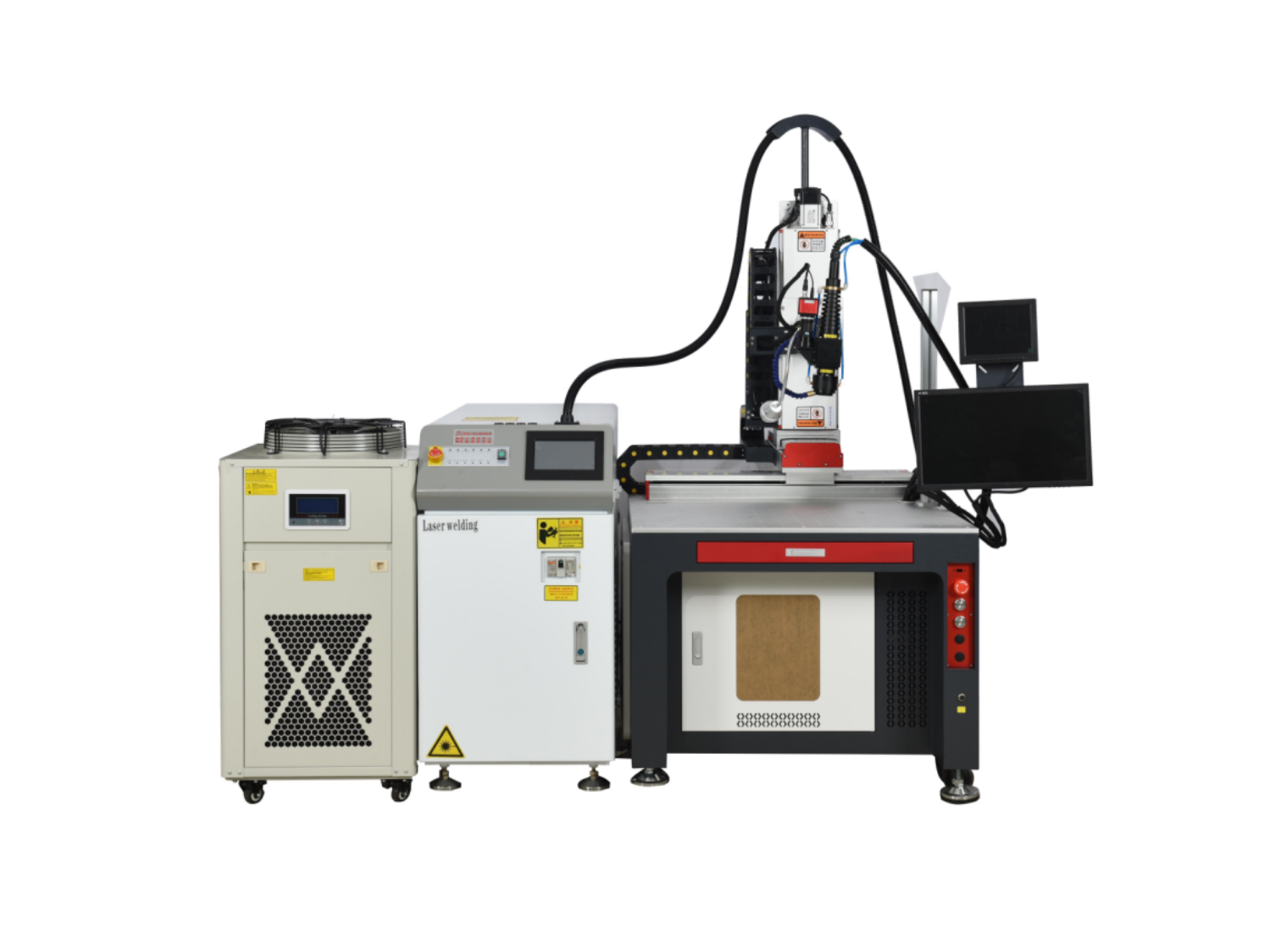


































 Cutter News
Cutter News