- No.609, Centre Of Huijin Nanxiang, Yinxiang Road, Nanxiang Town, Jiading District, Shanghai, China
- sherry@sanmachines.com
- +86-18616767021
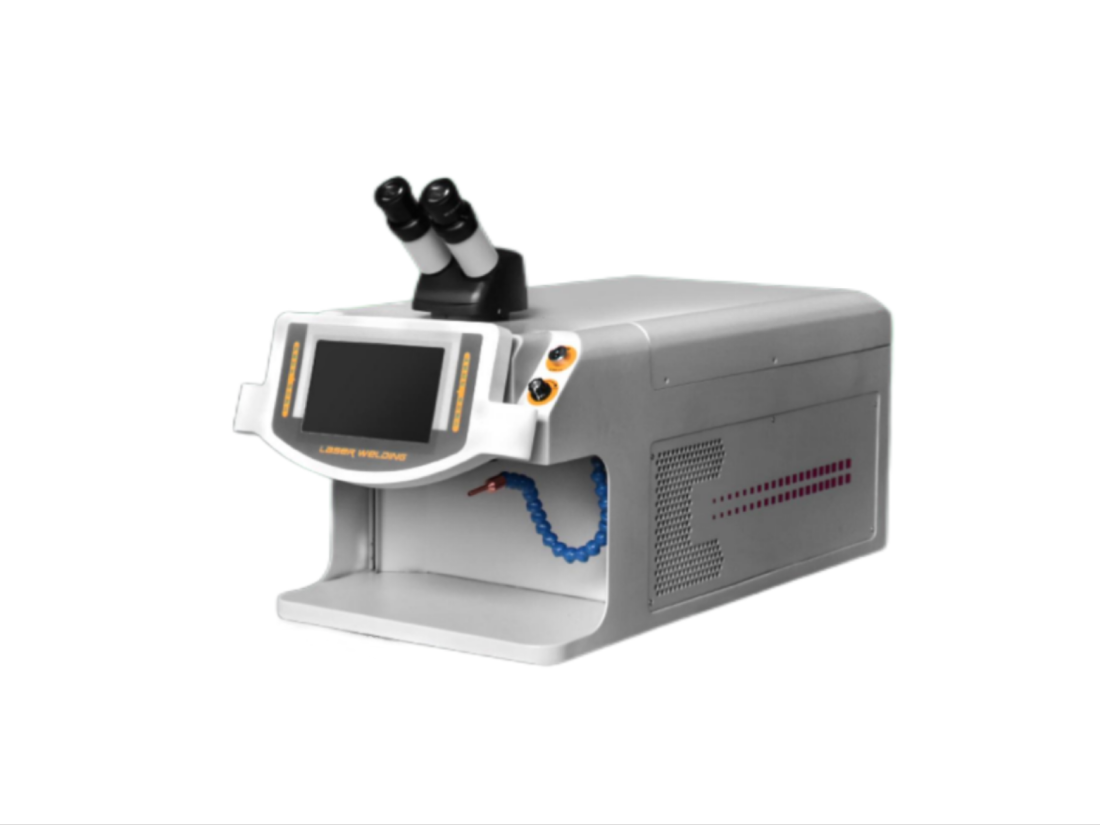
Market Analysis and Development Trends of Laser Mold Welding Machines (as of 2024-2025)
1. Market Overview
Global Market Size: The global laser mold welding machine market was valued at approximately $1.2 billion in 2024, with a projected CAGR of 7.5% (2025-2030), driven by demand from automotive, aerospace, and precision manufacturing sectors.
Key Regions:

Asia-Pacific dominates (45% market share), led by China, Japan, and South Korea, due to rapid industrialization and mold repair needs
Europe (30%) and North America (20%) focus on high-precision applications and automation.
2. Key Applications
Mold Repair & Maintenance: Laser welding is widely used to repair high-value injection molds, die-casting molds, and stamping molds, reducing downtime and costs by 30-50%.
Automotive: Critical for welding complex mold components (e.g., engine parts, gear molds) with minimal heat distortion.
Aerospace: Used for titanium alloy and nickel-based superalloy molds requiring ultra-high precision.
Electronics: Micro-welding for semiconductor molds and precision stamping die.
3. Technological Trends
Fiber Laser Dominance: Fiber lasers (wavelength1μm) hold 65% market share due to high efficiency, compact design, and lower maintenance.
Automation Integration: Adoption of AI-driven robotic arms and real-time monitoring systems (e.g., seam tracking) improves welding accuracy by 20-30%.
Hybrid Welding: Combining laser with arc welding (e.g., laser-TIG) enhances speed and penetration for large molds.
Additive Manufacturing: Laser metal deposition (LMD) for mold surface modification and 3D printing of complex mold structure.
4. Competitive Landscape
Top Players: TRUMPF (Germany), IPG Photonics (US), Han’s Laser (China), Amada (Japan), and Coherent (US) control 60% of the high-end market.
Chinese Manufacturers: Gaining traction with cost-effective solutions (e.g., 10-30% cheaper than European counterparts), targeting emerging markets in Southeast Asia and Africa.
5. Challenges
High Initial Cost: Entry-level systems cost $50k-$100k, limiting adoption in SMEs.
Skill Gap: Requires specialized operators for parameter debugging (e.g., pulse frequency, shielding gas selection).
Material Limitations: Challenges in welding highly reflective materials (e.g., copper alloys) and ultra-thick molds (>30mm).
6. Growth Opportunities
Emerging Economies: Rising mould requirements in India, Vietnam, and Mexico due to manufacturing relocation.
Sustainability: Laser welding reduces material waste by 15-20% compared to traditional methods, aligning with ESG goals.
Customized Solutions: Demand for modular systems for niche applications (e.g., medical device molds).
Conclusion
The laser mold welding market is poised for steady growth, driven by automation, material innovation, and repair applications. Manufacturers should prioritize R&D in multi-wavelength lasers and user-friendly software to capture opportunities in Asia-Pacific and green manufacturing sectors. Collaboration with mould service providers and vocational training programs will help overcome skill barriers.
Get professional support now
Related product links


































 Welder News
Welder News