- No.609, Centre Of Huijin Nanxiang, Yinxiang Road, Nanxiang Town, Jiading District, Shanghai, China
- sherry@sanmachines.com
- +86-18616767021
Parameters affecting the welding effect of laser welding machine!
Laser welding machines have gradually entered the market, replacing traditional welding methods. Laser welding technology is applied to many manufacturing processes, and laser welding technology is constantly improving, and the process is becoming more and more perfect. So what factors affect the effect of laser welding?

The parameters that directly affect the quality of laser welding machines include:
The energy of the laser pulse, the diameter of the laser beam spot, the pulse width of the laser, the frequency of the laser pulse, the pulse waveform of the light, the relative light absorption rate of the welded material, the welding speed, the shielding gas, etc.
Parameters affecting the welding effect of laser welding machines:
a) Laser spot focus diameter:
This is an extremely important parameter that reflects the design performance of the laser, and the unit is (mm). It determines the laser power density and processing range of the laser welding machine. If the optical design of the laser is reasonable and advanced, the laser energy is concentrated, and the focus is accurate, the laser spot diameter can be controlled within the range of 0.2mm-2mm, and whether the laser focus diameter can be controlled within 0.2mm is a strict test for the laser generator. Domestic lasers are generally designed to reduce costs. Therefore, the laser device processing is simple and the design is not rigorous. The laser diverges severely in the resonant cavity, making it difficult to focus accurately. The laser spot diameter output by the laser does not reach the nominal 0.2mm at all, but can only reach a minimum of 0.5mm. Due to the divergence of the laser, the output laser beam cannot be a regular circle, which causes the actual laser irradiation area to be too large, resulting in the phenomenon of ablation of the weld, that is, unnecessary laser irradiation at both ends of the weld, causing the weld to be concave. This phenomenon is particularly serious for repairing polished molds, and sometimes even causes the mold to be scrapped. Minglei Laser's lasers are well designed, strictly selected, and carefully debugged, so that the beam spot diameter output by the laser can be precisely monitored, so that the size of the focused spot can be as small as 0.2mm, and can be adjusted steplessly within the range of 0.2mm and 2mm, reaching the international advanced level.
b) Frequency of laser pulses of laser welding machine
This reflects the ability of the laser to emit how many pulses in one second, and the unit is (Hz). First of all, it should be noted that welding metal uses the energy of laser. When the laser power is constant, the higher the frequency, the smaller the energy output of each laser. Therefore, we need to consider the processing speed while ensuring that the laser energy is sufficient to melt the metal to determine the output frequency of the laser. In the case of laser repair of molds, 15Hz can already meet the needs of welding. Too high a frequency will inevitably cause the laser pulse energy to be too low, resulting in welding failure.
c) Energy of laser pulse
Refers to the maximum output energy of a single laser pulse, in J (joule). This is a major parameter of the laser, which determines the maximum energy that the laser welding machine laser can generate. According to the purpose of mold repair, laser energy below 70J can already meet the needs of any occasion. Any larger energy is in vain or cannot be used at all, and it will lead to the continuous increase of the volume of the laser power supply and the heat sink, reducing the efficiency of the power supply.
d) Laser pulse waveform and relative light absorption rate of the welded material
For laser welding machines that use pulsed lasers for welding, the laser pulse waveform is an important issue in pulsed laser welding.
When a high-intensity laser is incident on the surface of a material, the metal surface will reflect 60% to 98% of the laser energy, and the reflectivity changes with the surface temperature.
Therefore, different metals have different reflectivity and utilization rates for lasers. To perform effective welding, lasers with different waveforms must be input so that the metal structure at the weld can crystallize in the best way and form a structure consistent with the base metal, thus forming a high-quality weld.
Related product links
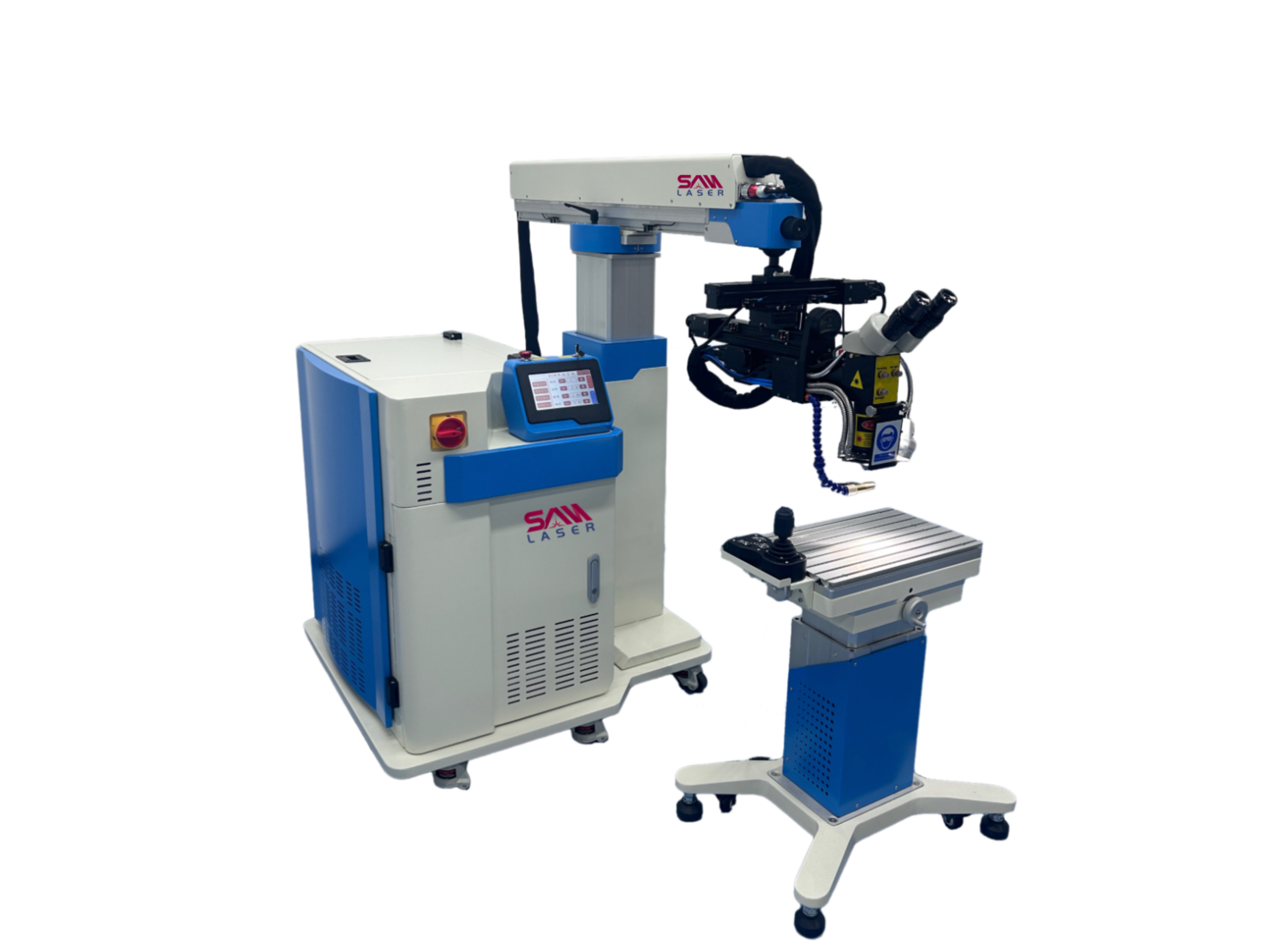
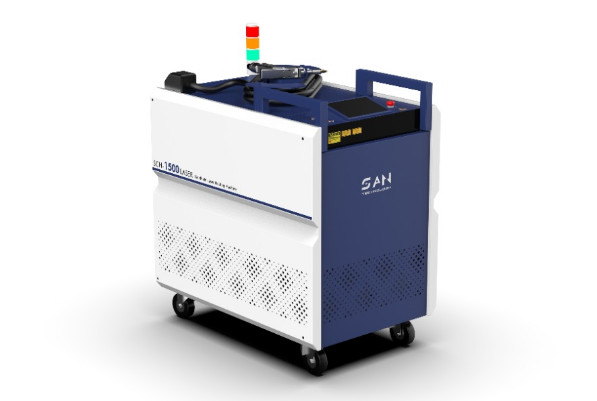
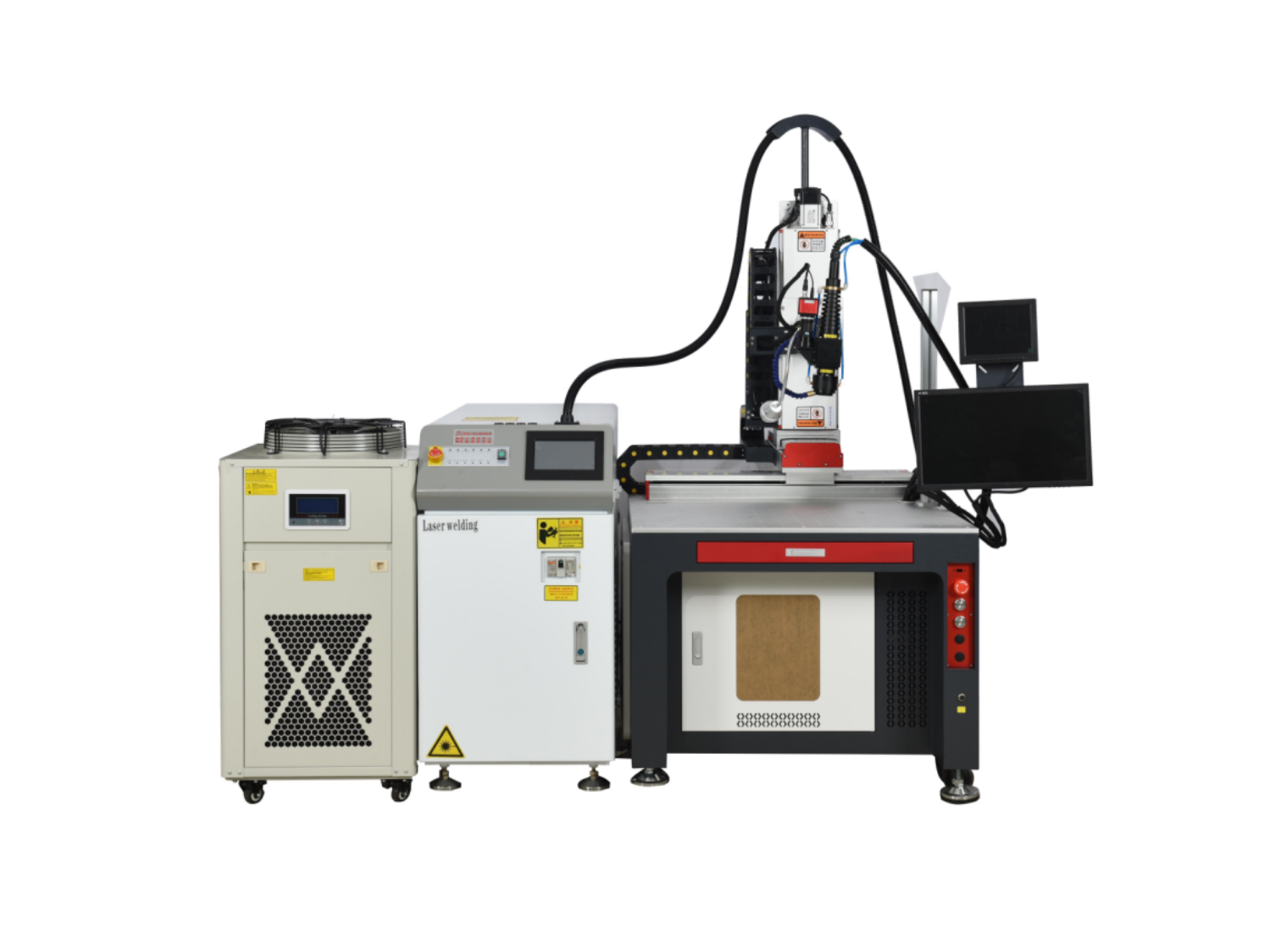
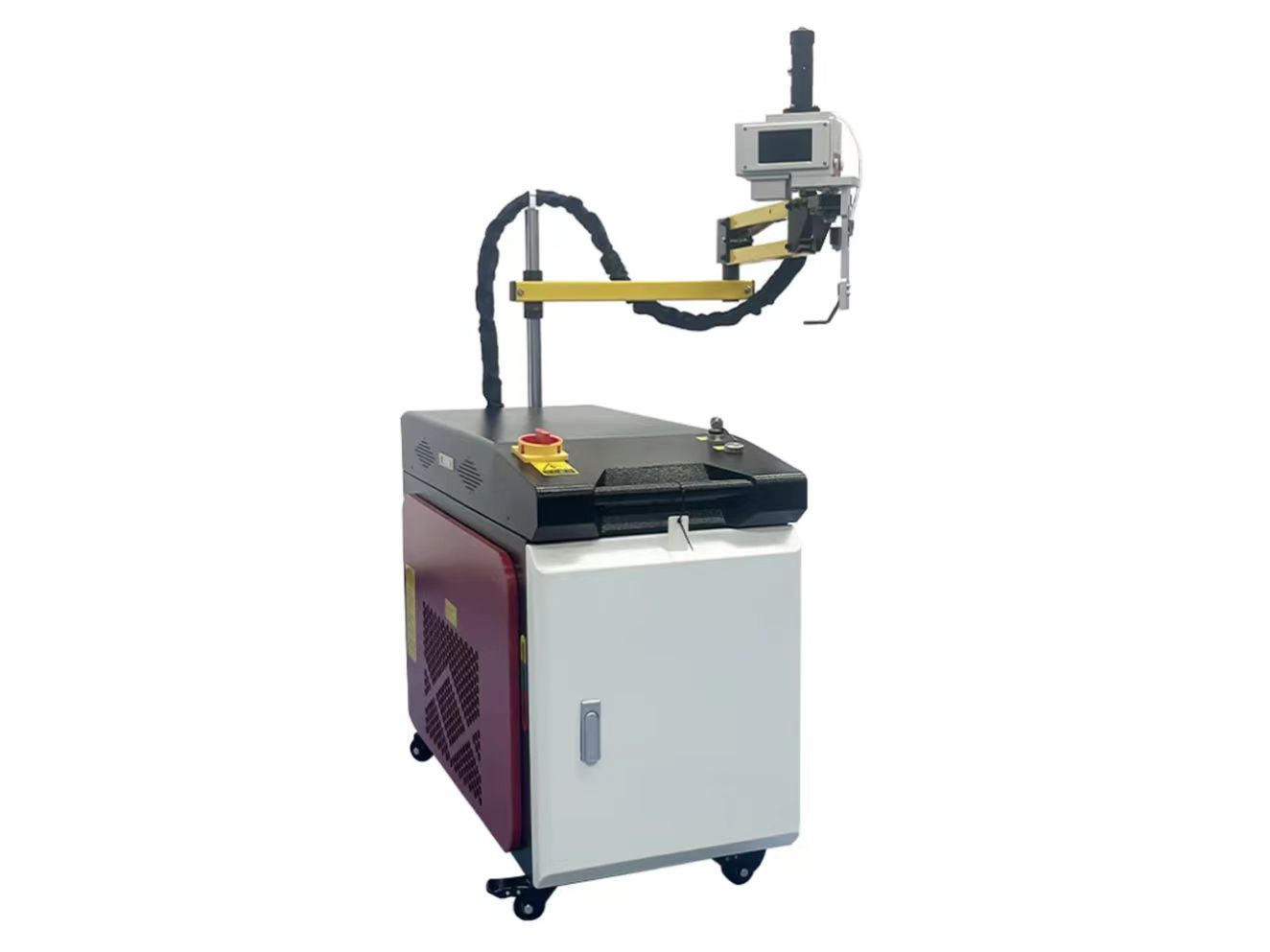
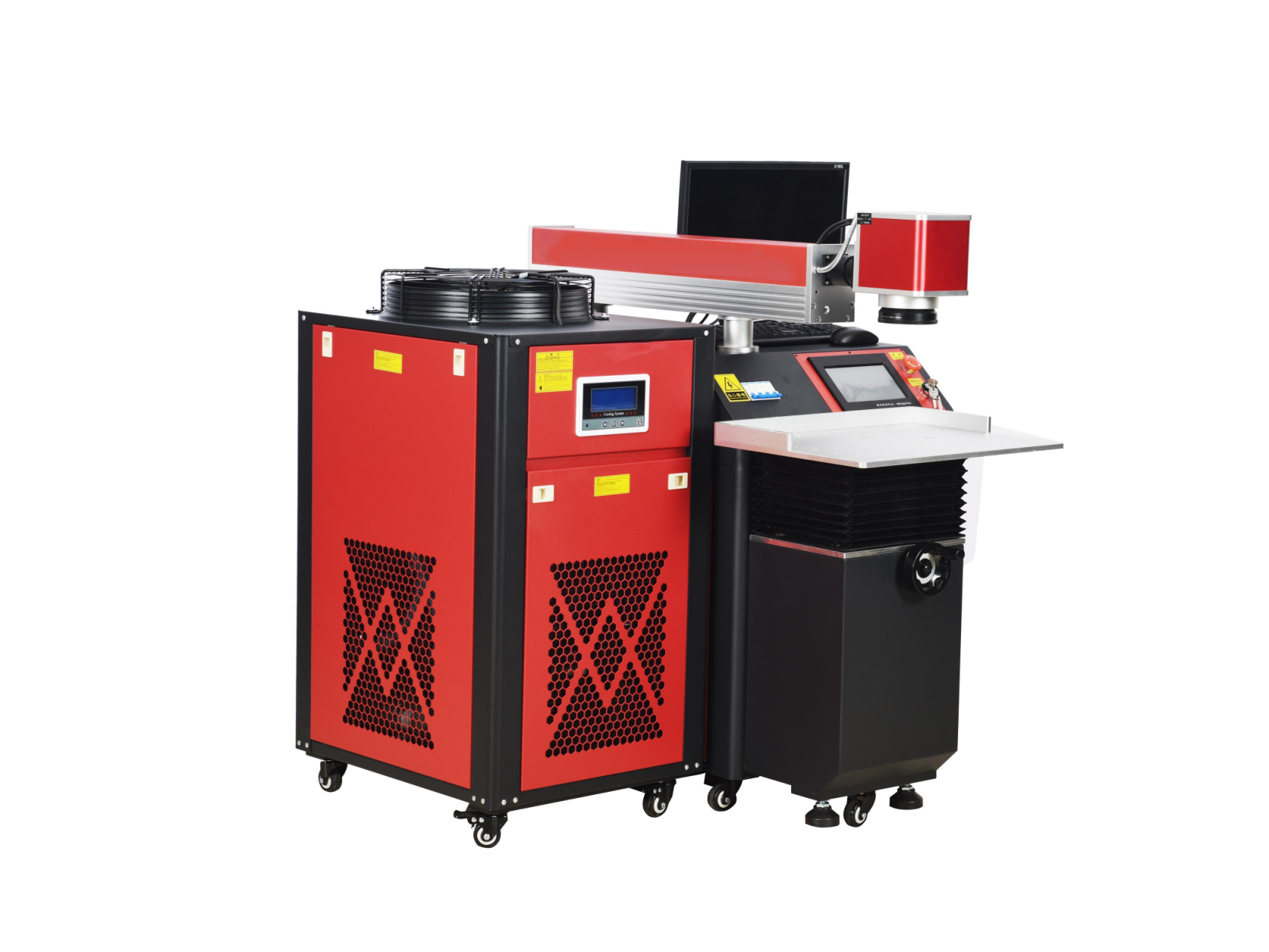
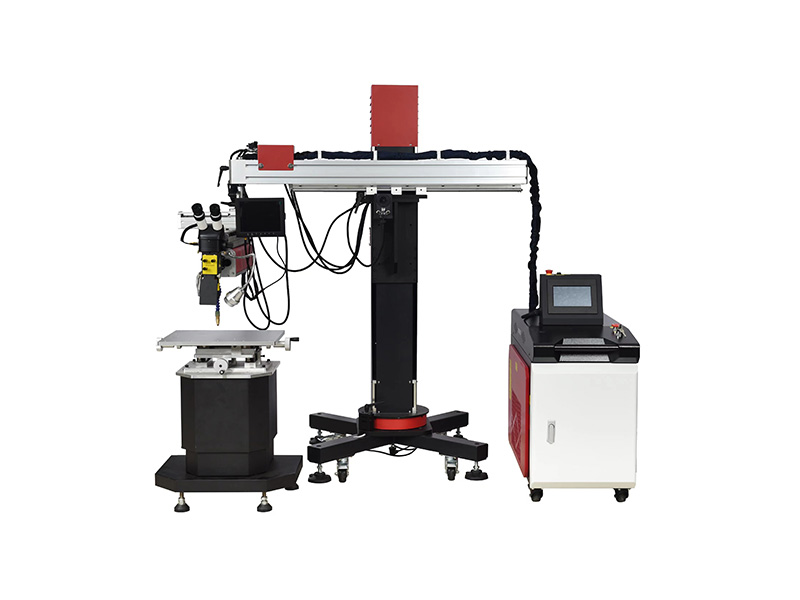
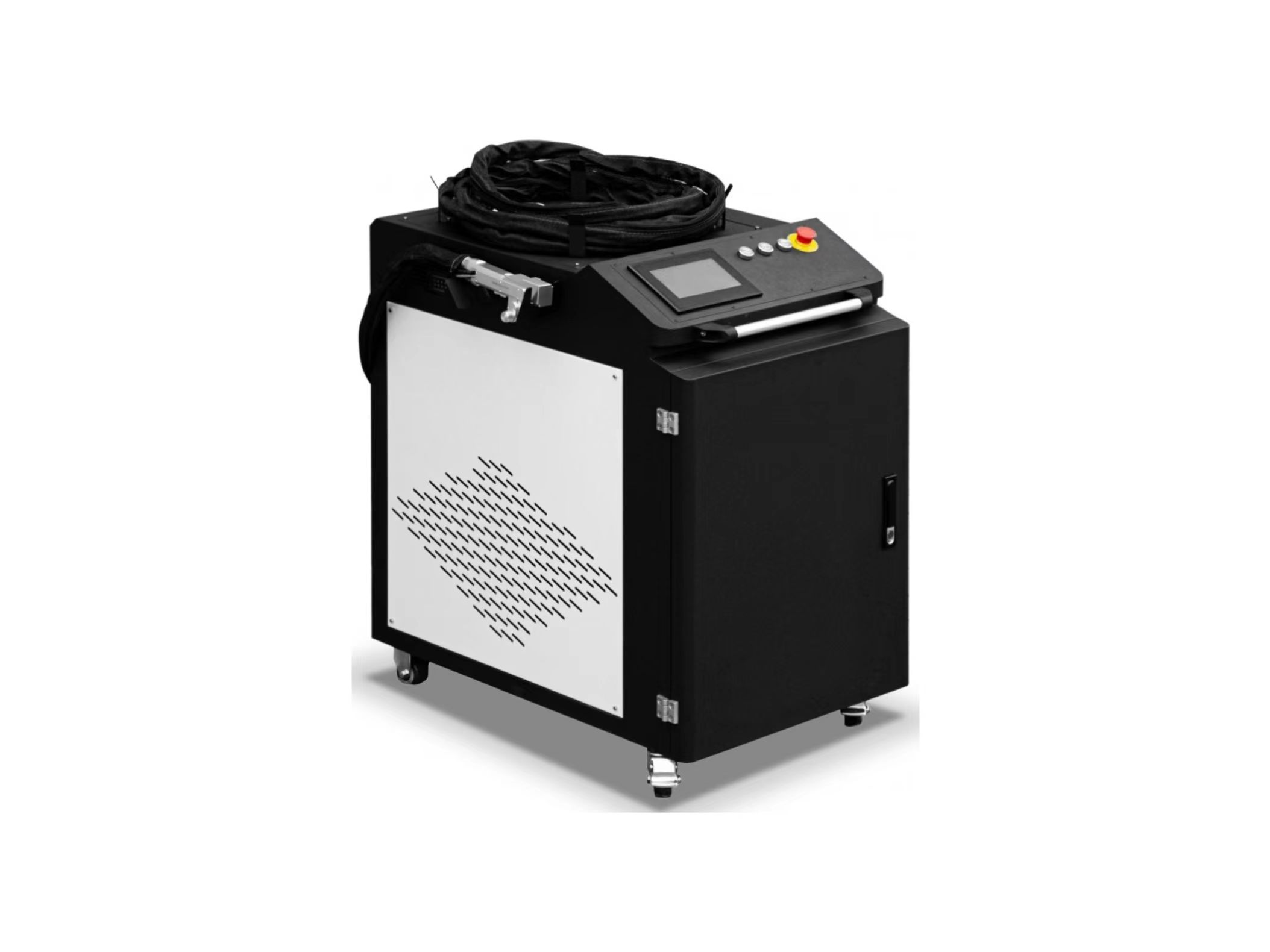
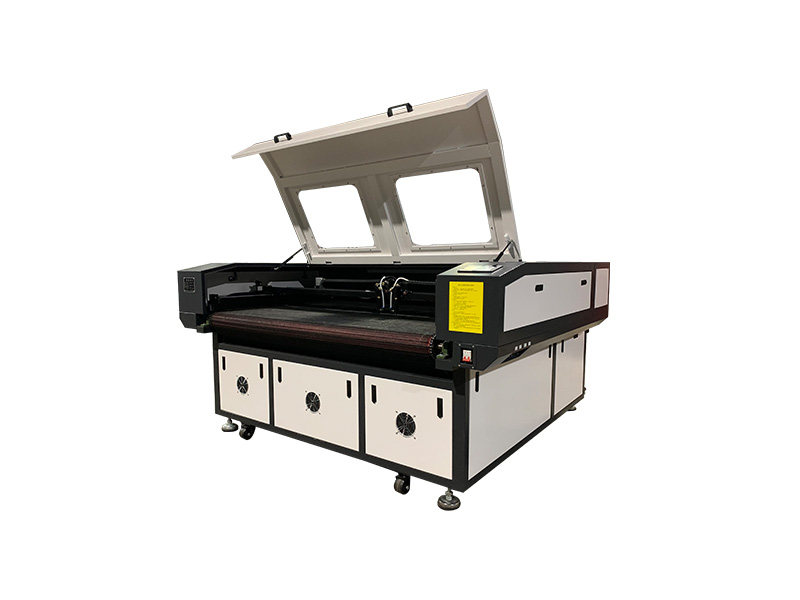

































 Welder News
Welder News