- No.609, Centre Of Huijin Nanxiang, Yinxiang Road, Nanxiang Town, Jiading District, Shanghai, China
- sherry@sanmachines.com
- +86-18616767021
The future of welding!
Continuous advances in technology, automation, materials science, and environmental sustainability define the future of welding. As the industry evolves, welding processes and technologies are constantly adapting to new challenges and opportunities. Here are some key trends and developments that could impact the future of welding:
1. Automation and Robotics
Increasing Automation: The convergence of robotics and automation in welding is accelerating. Automated welding systems can perform consistent, high-quality welds, thereby increasing efficiency, reducing labor costs, and minimizing human error.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): These robots are designed to work alongside human welders to help with repetitive or complex tasks. Cobots are easy to use and can increase productivity while keeping workers out of hazardous environments.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Advanced sensors and artificial intelligence can analyze and optimize welding parameters in real time, allowing for more precise control of the welding process and minimizing defects. AI can also predict potential problems before they occur, reducing downtime and rework.
2. Laser Beam Welding
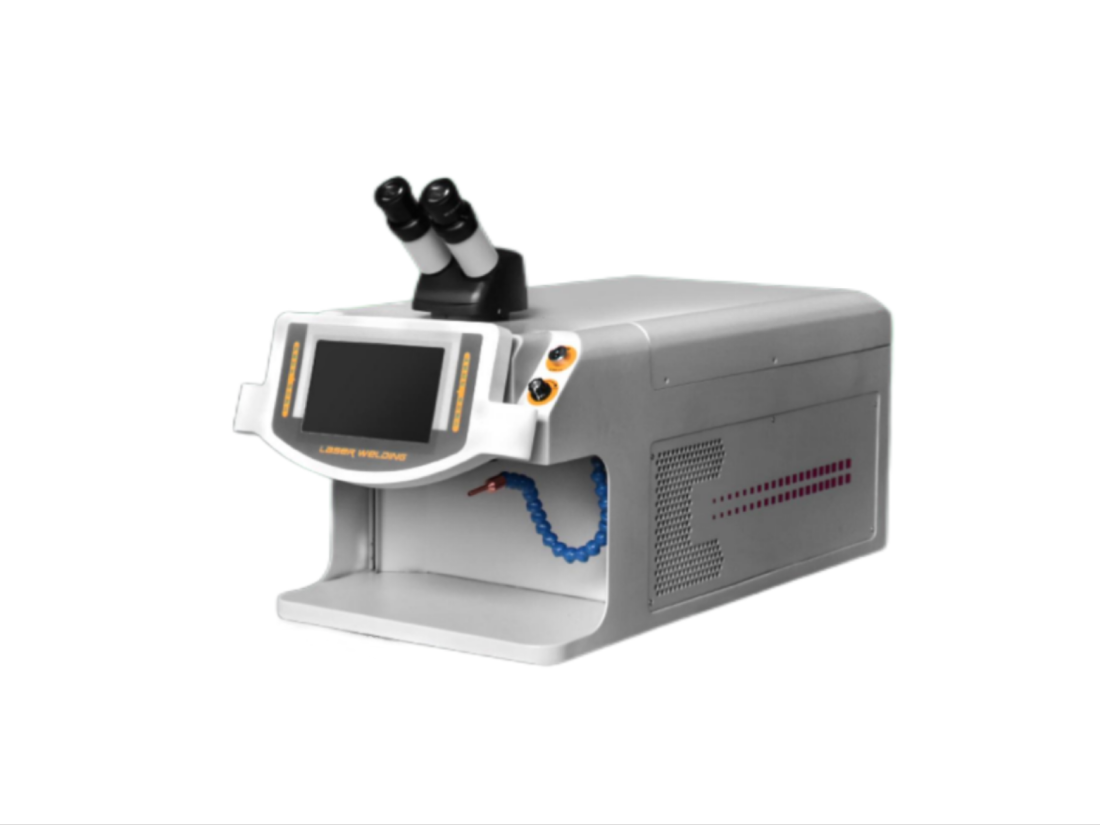
Laser Welding: Laser technology offers high precision and speed, enabling the welding of thinner materials and complex geometries. Laser welding also minimizes thermal distortion, which is a significant advantage, especially in the automotive and electronics industries.
Electron beam welding: This process uses a focused, high-speed electron beam to weld materials in a vacuum. The process features deep penetration and high precision, making it suitable for industries such as aerospace that require strong, reliable welds.
3. Hybrid welding technology
Process combination: Hybrid welding is the integration of two or more welding processes, such as laser welding and MIG welding, into a single system. This combination improves weld quality, speed, and flexibility, resulting in improved performance of complex components.
Multi-process welding: The future may see an increase in hybrid and multi-process welding systems, allowing for greater manufacturing flexibility.
4. Advanced materials and welding technology
Welding of new materials: As industry moves toward lighter, stronger, and more specialized materials, such as advanced high-strength steels, titanium alloys, and composites, welding technology will continue to evolve to accommodate these materials. New processes will be developed to effectively join these challenging materials while maintaining their integrity.
Dissimilar material welding: There is a growing need to weld dissimilar metals, such as aluminum and steel. New technologies and filler materials are being developed to overcome the challenges of bonding materials with different thermal properties, expansion rates, or chemical compositions.
5. Sustainability and environmentally friendly practices
Energy-efficient welding: Future welding technologies will focus on reducing energy consumption and environmental impact. For example, efficient welding machines and processes that use less energy and reduce heat distortion are becoming increasingly popular.
Recycling and reuse: Recycling materials and minimizing waste in the welding process are key to more sustainable practices. Innovations in welding consumables that reduce waste and are reusable will help reduce the environmental impact of welding operations.
Zero-emission welding: In response to stricter environmental regulations, there will be an increasing demand for welding processes that reduce emissions, such as fume extraction systems and more environmentally friendly shielding gases.
6. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR)
Training and simulation: VR and AR technology will play an important role in future welding training. VR welding simulators allow welders to practice without physical materials, helping to reduce training costs and improve skills.
Enhanced welding guidance: AR technology can provide operators with real-time welding guidance, displaying instructions or overlaying key information directly onto the workpiece, improving accuracy and reducing errors.
7. Smarter welding equipment
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT-enabled welding equipment will allow machines to connect to the internet, providing real-time data for monitoring and troubleshooting. Welders can remotely monitor welding parameters, maintenance schedules, and performance metrics, improving uptime and operational efficiency.
Predictive maintenance: IoT-connected welding machines can predict when maintenance is needed, reducing unplanned downtime and extending equipment life.
8. Improving safety standards and protective gear
Welder exoskeletons: Wearable robotic exoskeletons are being developed to help welders lift heavy objects and reduce the stress of long work hours. These wearables help prevent injuries and improve worker comfort.
Advanced PPE: Future improvements in personal protective equipment (PPE) are likely, such as more comfortable, lightweight, and durable welding helmets with better visibility and integrated air filtration systems to provide safer working conditions.
9. Globalization and the need for a skilled workforce
Global demand for skilled welders: As industries such as manufacturing, construction, and renewable energy continue to grow around the world, the demand for skilled welders will increase. Advanced training programs and certification processes will become more important to ensure the workforce is prepared for new technologies and welding techniques.
Remote welding: Remote welding may become more common in some industries, where a skilled operator can remotely control a welding robot or automated system, allowing work in dangerous or hard-to-reach places.
Related product links
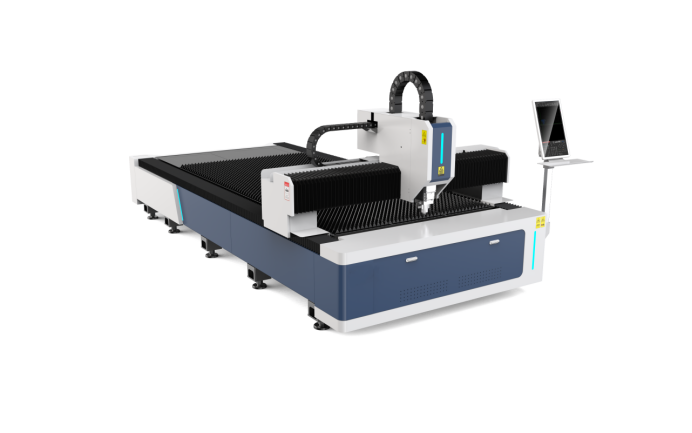


































 Welder News
Welder News